the Ecco Project
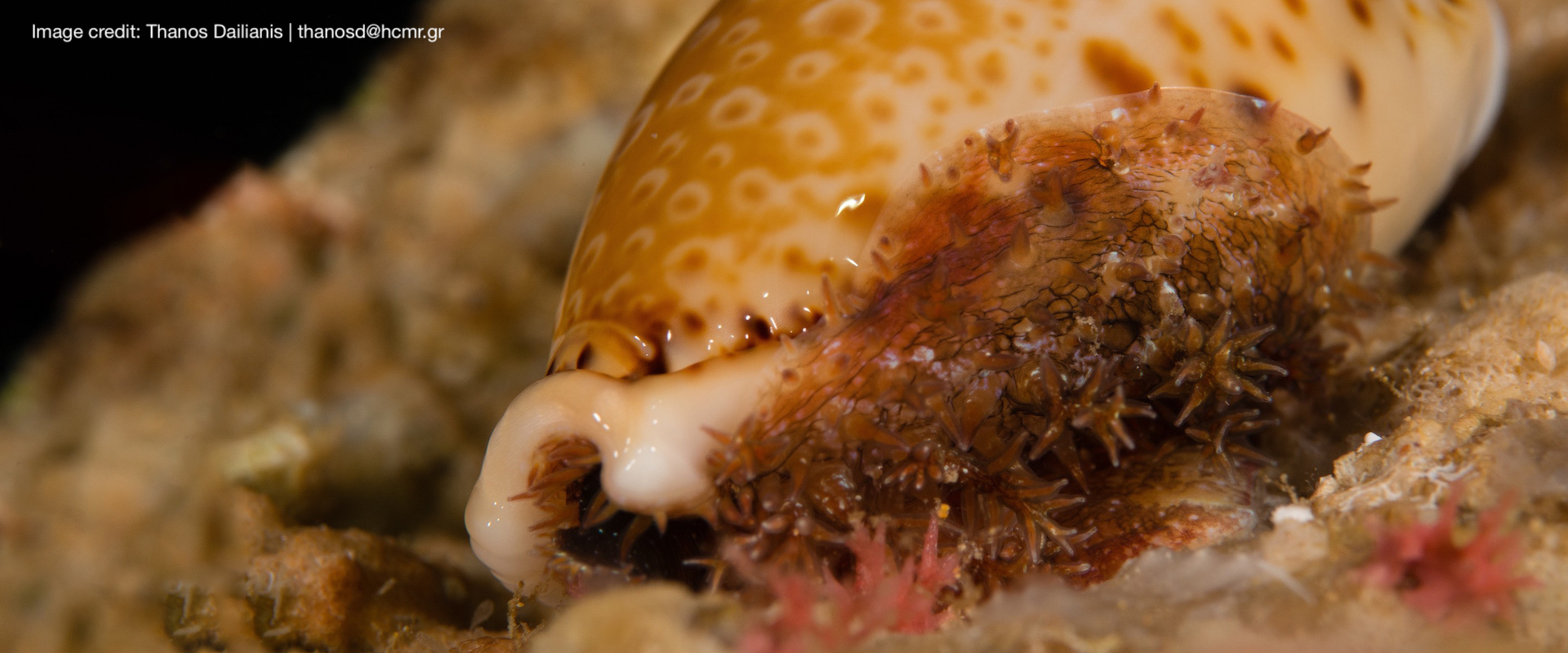
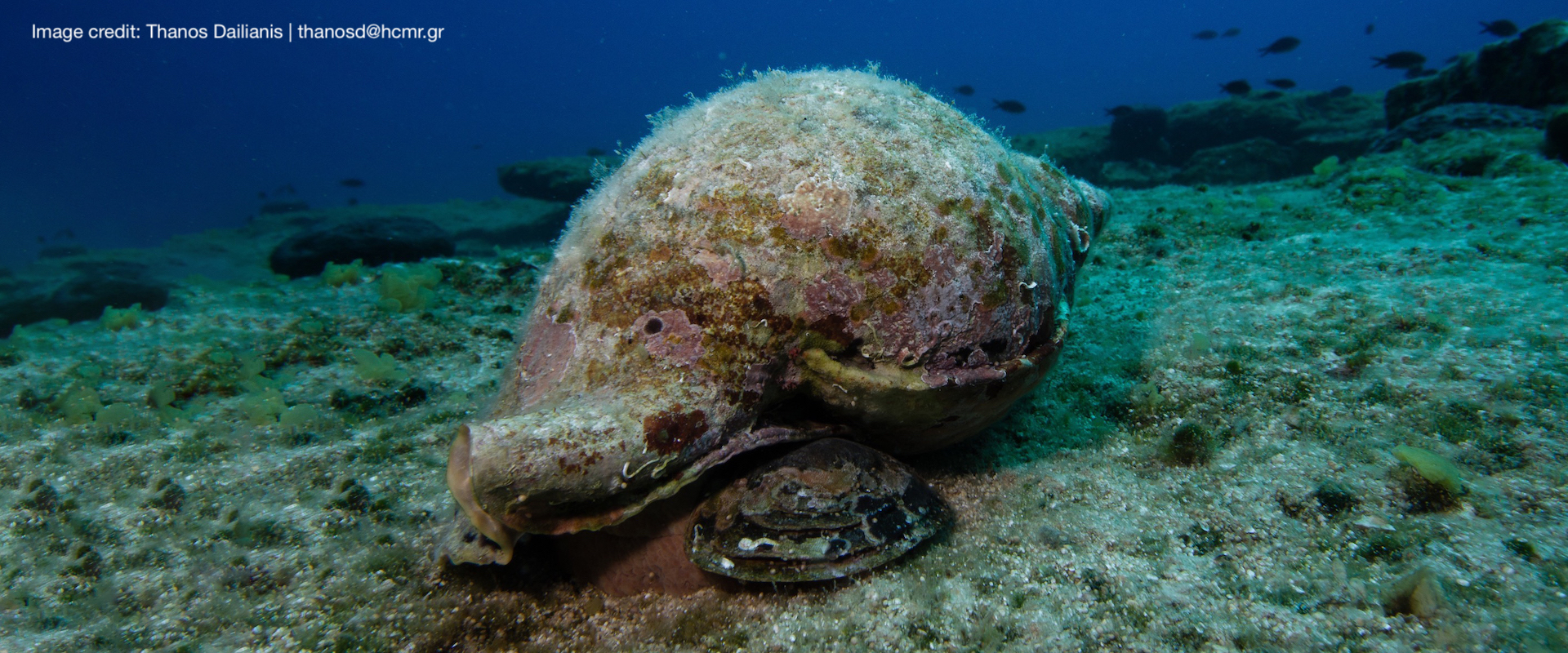
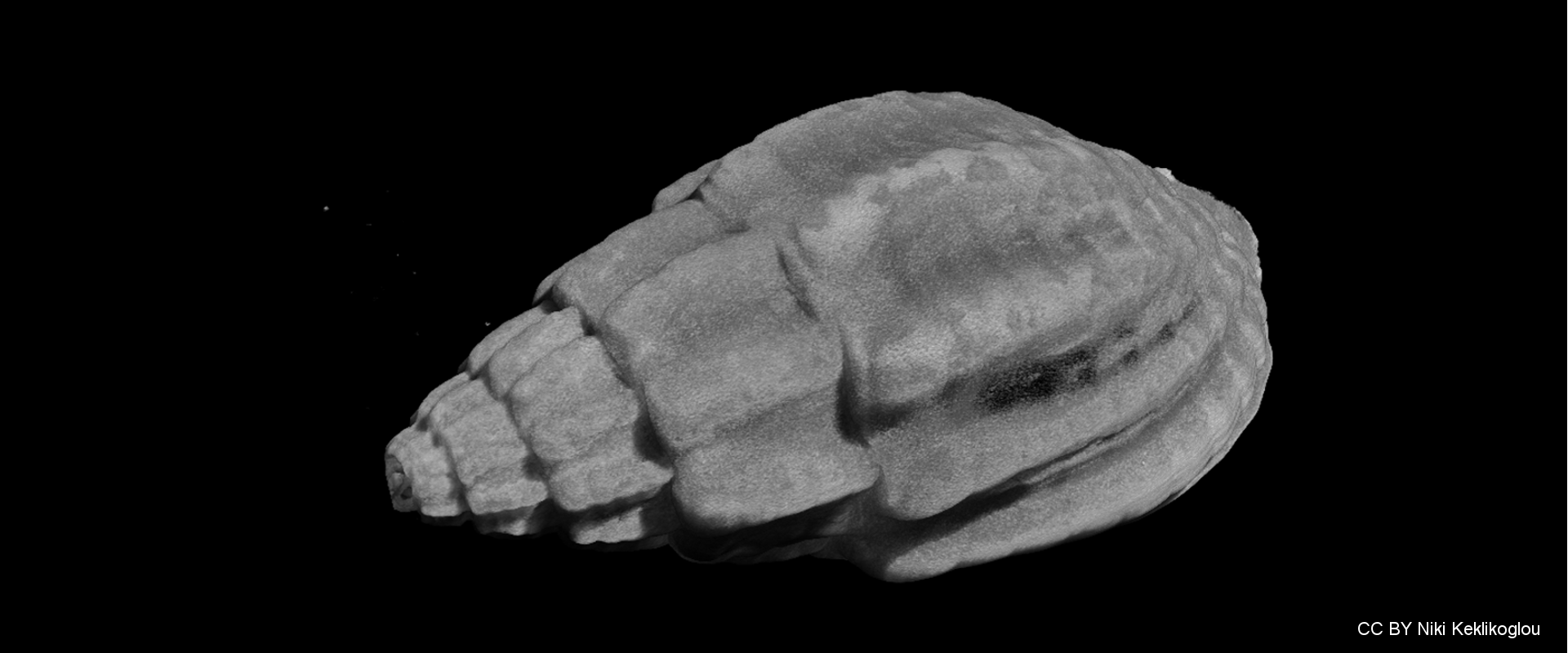
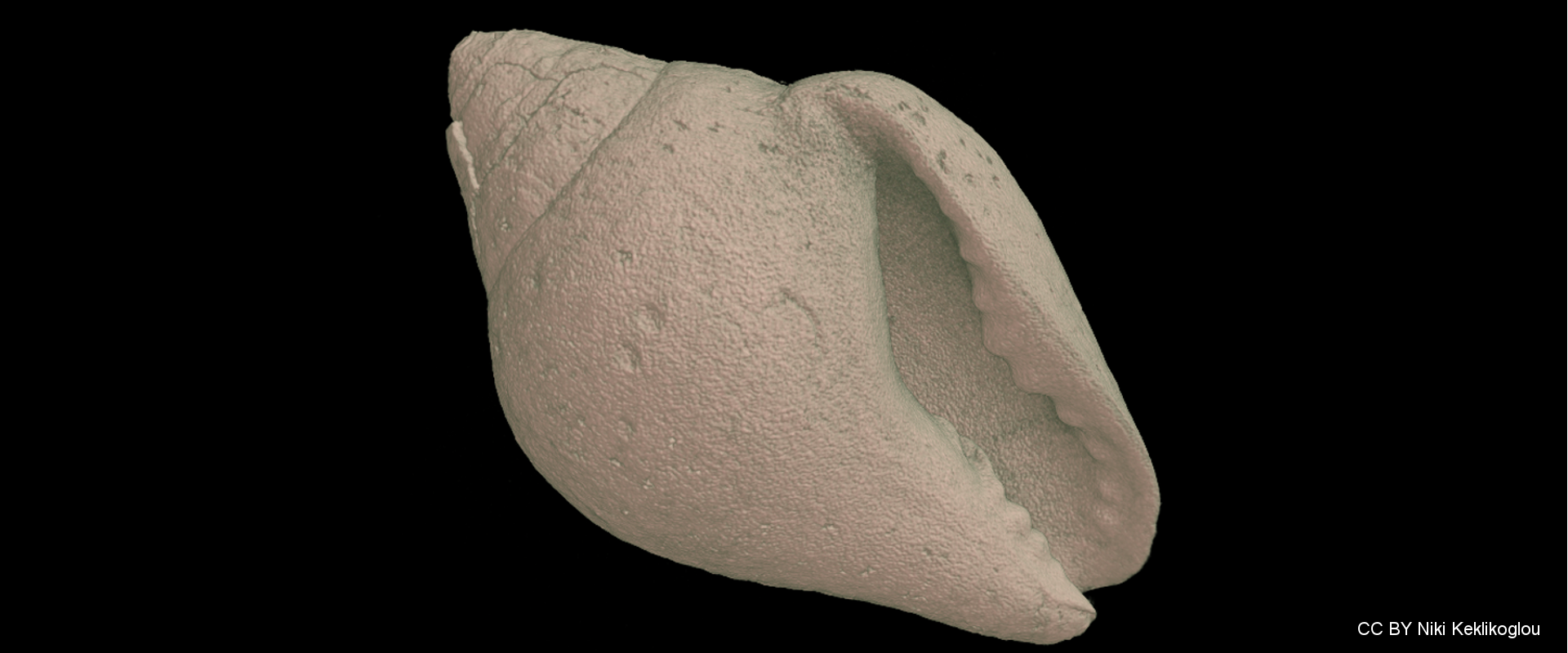
 Anthropogenic activities, such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, are responsible for the increase of atmospheric carbon dioxide, which in turn is absorbed by the oceans causing changes in seawater carbonate chemistry. Ocean acidification (low pH) decreases the calcium carbonate saturation states in seawater, thus inhibiting calcification rates in shell-forming marine organisms. Elevated carbon dioxide may have additional sublethal impacts on organismal, developmental and physiological levels and as a result can significantly suppress the abundance and diversity of species.
Anthropogenic activities, such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, are responsible for the increase of atmospheric carbon dioxide, which in turn is absorbed by the oceans causing changes in seawater carbonate chemistry. Ocean acidification (low pH) decreases the calcium carbonate saturation states in seawater, thus inhibiting calcification rates in shell-forming marine organisms. Elevated carbon dioxide may have additional sublethal impacts on organismal, developmental and physiological levels and as a result can significantly suppress the abundance and diversity of species.
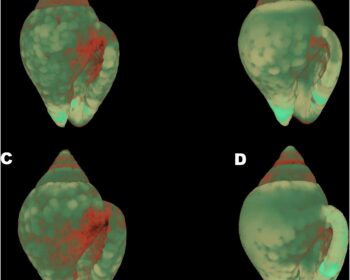
Four different experimental treatments are planned during the ECCO Project using a combination of low or ambient pH and increased or ambient temperature in order to investigate the long-term synergistic effects of those two factors on marine gastropods. An integrated multi-disciplinary approach is used to investigate morphological, physiological, behavioral, chemical and molecular responses of a selected gastropod species on a complementary basis. A long term experiment (one year) is scheduled in order to investigate the direct and indirect effects of low pH and increased temperature and also to reveal possible adaptations of the organisms. The methodology will include scanning of calcified structures with a micro-computed tomograph (micro-CT), advanced analysis of 3D models, Confocal Raman Microscopy for CaCO3 polymorphs and real-time PCR gene expression analysis.